- Interest Coverage Ratio:
This ratio measures a company’s ability to pay interest on its outstanding debt. It’s calculated by dividing EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) by the interest expenses. A higher ratio indicates that a company can comfortably meet its interest obligations, while a lower ratio suggests potential financial strain. - Debt to Equity Ratio:
This ratio compares a company’s total debt to its shareholders’ equity. It shows how much debt is used to finance the company relative to its equity base. A higher ratio indicates higher leverage, meaning the company relies more on debt to fuel growth, which can increase risk. - Debt to Asset Ratio:
This ratio indicates the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed through debt. It is calculated by dividing total debt by total assets. A higher ratio suggests that a larger portion of the company’s assets are financed by creditors, which can be a sign of higher financial risk. - Financial Leverage Ratio:
Financial leverage ratio refers to the degree to which a company uses borrowed money (debt) to finance its operations. It’s calculated by dividing total assets by total equity. A higher leverage ratio means the company is more dependent on debt to run its business, which can amplify both potential returns and risks.

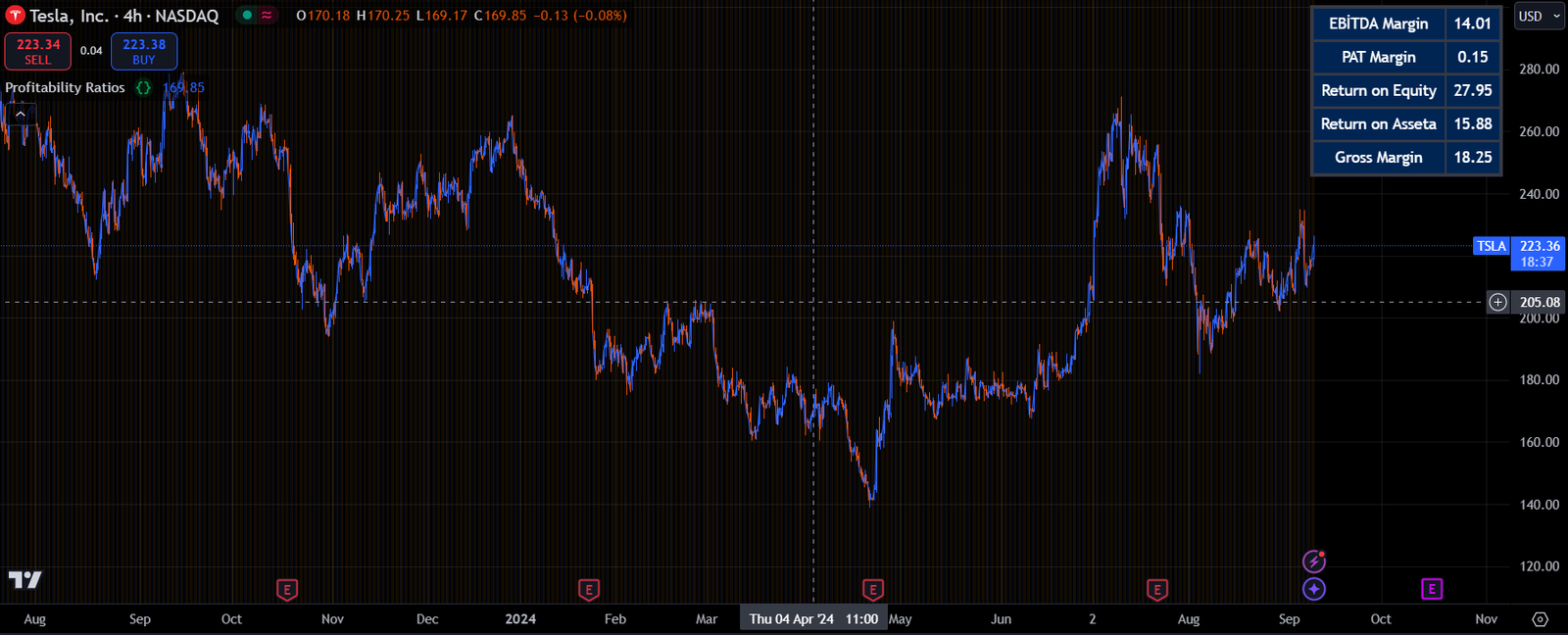
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.